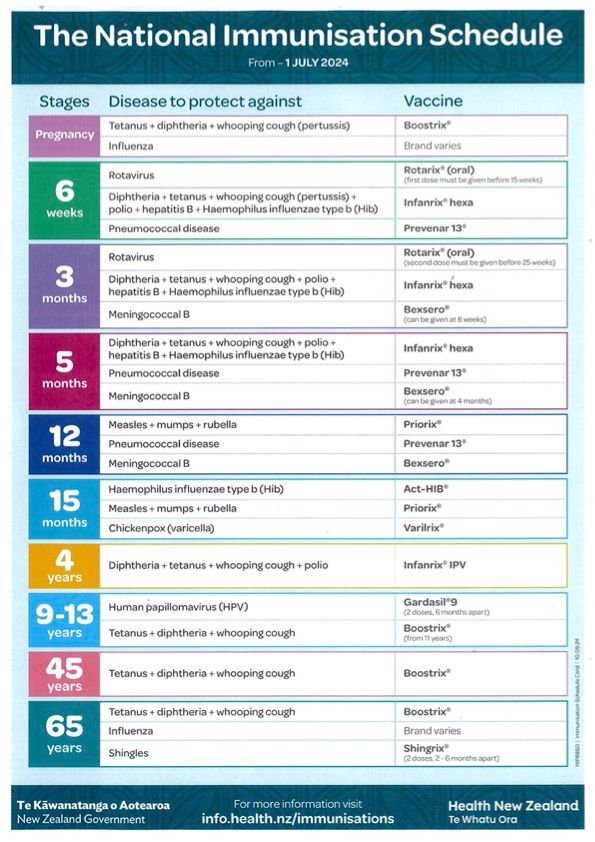
National Immunisation Schedule
Lots of vaccines are free and for Tamariki under 18, all immunisations on the National Immunisation Schedule are free, no matter what your visa or citizenship status is, this includes visitors to Aotearoa New Zealand.
- Lots of vaccines are also free for adults, including measles. Some you have to pay for if you do not meet certain criteria.
- If you are pregnant the whooping cough and flu vaccines are free.
You may need to pay for extra vaccines that are not on the schedule, like travel vaccines.
Please check when booking an immunisation to confirm whether there is a cost for you.
Vaccines
All vaccines available in New Zealand are licensed for use in this country.
Vaccines on the New Zealand National Immunisation Schedule are free when given as part of the Schedule. Other vaccines are not funded, but are available for purchase through your family doctor.
Last updated: 29/01/25
Varilrix® is used for primary vaccination of infants from nine months of age, children and adults to protect against varicella-zoster infection (chickenpox). The vaccine may prevent or reduce the severity of chickenpox disease if it is given within 3-5 days of exposure to someone with the disease.
A two dose course of Varilrix® is recommended and funded for individuals aged 9 months or older who have not have the disease or immunisation and who meet at least one of the eligibility criteria below:
- Who are HIV-positive with mild or moderate immunosuppression, on the advice of their specialist
- Prior to elective immunosuppressive therapy that will be longer than 28 days
- With chronic liver disease who may in future be candidates for transplantation
- With deteriorating renal function before transplantation
- Prior to solid organ transplantation
- After a haematopoietic stem cell transplantation, on the advice of their specialist
- After chemotherapy, on the advice of their specialist
- With an inborn error of metabolism at risk of major metabolic decompensation,
- Who are a household contact of a child or adult patient who is immunocompromised or undergoing a procedure leading to immunocompromise, where the household contact has no clinical history of varicella infection of immunisation

